Vaatafwijkingen (
vascular anomalies)
zoals
hemangiomen (
infantiele
hemangiomen, hemangioma of infancy) en
vasculaire malformaties
ontstaan meestal op jonge leeftijd. Hemangiomen zijn vaak afwezig of nog klein
bij de geboorte en groeien snel de eerste maanden. Vasculaire malformaties zijn
aanwezig bij de geboorte, en groeien in proportie met het kind mee. Hemangiomen
kunnen ook op oudere leeftijd ontstaan, bij volwassenen (
angioma
senilis,
verkregen hemangiomen).
De (aangeboren) vaatafwijkingen worden onderverdeeld in
vasculaire
tumoren, zoals het infantiel hemangioom, en
vasculaire
malformaties, zoals de wijnvlek of de ooievaarsbeet. Zie ook
de
ISSVA classificatie onder in deze
pagina.
Vasculaire malformatiesVasculaire malformaties
worden onderverdeeld in
low flow malformaties (capillair,
veneus, lymfatisch, of gemengde laesies) en
high flow malformaties
(met een arteriële aanvoer). De meeste malformaties bestaan uit één vaattype
(capillair, veneus, of lymfatisch). Arterioveneuze malformaties bevatten een
combinatie van arteriële, capillaire en veneuze componenten. Malformaties met
twee of meer verschillende componenten worden
combined vascular
malformations genoemd.
Capillaire malformaties
Capillaire malformaties komen het meest voor en bestaan uit gedilateerde capillairen,
arteriolen en/of venulen in de huid of mucosa. Een
naevus flammeus
(wijnvlek) is een capillaire malformatie. Een
naevus flammeus bestaat uit roze rode
wegdrukbare macula, en is aanwezig vanaf de geboorte. Bij het ouder wordt de
laesie donkerder rood of paars en er kunnen ook dikkere gedeelten in komen.
Ze zitten vaak lateraal in het gelaat, of op ledematen of op de romp en gaan
niet over de middellijn heen. Bij een periorbitale naevus flammeus kan glaucoom
voorkomen. Een naevus flammeus kan onderdeel zijn van het
Sturge-Weber
syndroom of het
Klippel-Trenaunay syndroom.
Ook de
naevus van Unna (salmon patch), een lichtroze
macula midden in de nek (
ooievaarsbeet)
of op het voorhoofd (‘angel kiss’) is een capillaire naevus. Anders dan een
wijnvlek gaan deze laesies, vooral die op het voorhoofd, meestal in regressie
in de eerste 2 levensjaren. Multipele ronde capillaire malformaties verspreid over het lichaam kunnen voorkomen bij een
RASA1 mutatie. Soms komen daarbij ook arterioveneuze malformaties of fistels voor, vandaar de naam
capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndroom (
CM-AVM syndroom).
Teleangiëctasieën zijn
ook capillaire malformaties. Ze kunnen congenitaal voorkomen, als geïsoleerd
verschijnsel maar ook in het kader van syndromen zoals het
Rendu-Osler-Weber
syndroom en andere
hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
(HHT) syndromen.
Teleangiëctasieën
komen ook op latere leeftijd voor,
idiopathisch, bij zwangerschap, of als onderdeel
van systeemziekten zoals sclerodermie en levercirrhose.
![Naevus flammeus (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Naevus flammeus](../../../images/naevus-flammeus-4z.jpg) |
![Naevus van Unna, ooievaarsbeet (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Naevus van Unna, ooievaarsbeet](../../../images/salmon-patch-2z.jpg) |
![Teleangiëctasieën bij levercirrhose (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Teleangiëctasieën bij levercirrhose](../../../images/teleangiectasieen-3z.jpg) |
| naevus
flammeus |
ooievaarsbeet |
teleangiëctasieën |
![Capillaire malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Capillaire malformatie](../../../images/capillaire-malformatie-1z.jpg) |
![Capillaire malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Capillaire malformatie](../../../images/capillaire-malformatie-2z.jpg) |
![Capillaire malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Capillaire malformatie](../../../images/capillaire-malformatie-3z.jpg) |
| capillaire
malformatie |
capillaire
malformatie |
capillaire
malformatie |
Veneuze malformatiesVeneuze malformaties zijn lichtblauwe
tot donkerblauwe zwellingen, eenvoudig comprimeerbaar. Ze zijn gelokaliseerd
in de huid en mucosa, maar kunnen ook in weke delen, spieren en inwendige organen
zitten. Meestal solitair, soms multipel of diffuus. Vaak zijn er mutaties in
het TIE2 gen. Bij andere typen veneuze malformaties zoals
glomuveneuze malformaties,
blue rubber bleb nevus syndroom en
cerebrale caverneuze malformaties zijn andere genen betrokken.
Glomuveneuze
malformaties zijn multipele roodpaarse nodi en plaques. De laesies
zijn vaster aanvoelend, minder comprimeerbaar en vaak pijnlijk bij aanraking.
Ze komen familiair voor en er is een mutatie in het glomuline gen. Bij
blue rubber bleb nevus syndroom zijn er multipele
kleine donkerblauwe rubberachtig aanvoelende veneuze malformaties.
Cerebrale caverneuze malformaties komen voor in de hersenen
en in het ruggenmerg en kunnen neurologische klachten veroorzaken. Ze zijn geassocieerd
met veneuze of capillaire malformaties in andere organen en in de huid.
Lymfatische malformatiesLymfatische malformaties
bestaan uit gedilateerde lymfevaten of cysten bekleed met lymfepitheel. Ze worden
onderverdeeld in
macrocysteus,
microcysteus
of
gemengd. Vaak gelokaliseerd in de hoofdhals regio,
die rijk is aan lymfvaten, maar ze kunnen overal voorkomen. Macrocysteuze lymfatische
malformaties (oude term:
cystic hygroma) zijn meestal
grote, cysteuze massa’s, vlak onder de huid liggend, soms dieper gelegen. Laesies
in de nekregio kunnen geassocieerd zijn met syndromen (Turner, Noonan en Down
syndroom). Microcysteuze lymfatische malformaties (oude term:
lymphangioma
circumscriptum) kunnen in alle weefsels voorkomen maar vooral
in de huid en mucosa. Het zijn multipele kleine, stevige, vaak gegroepeerde
heldere of hemorrhagische vesikels.
Angiokeratomen
zijn mogelijk ook lymfatische malformaties. Voorheen zijn ze altijd
beschouwd als capillaire malformaties, maar de vaatjes in
angiokeratomen kleuren aan met
D2-40, een specifieke lymfvat-marker.
![Lymphangioma circumscripta (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Lymphangioma circumscripta](../../../images/lymphangioma-6z.jpg) |
![Lymphangioma circumscripta (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Lymphangioma circumscripta](../../../images/lymphangioma-2z.jpg) |
![Lymfatische malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Lymfatische malformatie](../../../images/lymfatische-malformatie-1z.jpg) |
| cystic
hygroma |
lymphangioma
circumscripta |
lymfatische
malformatie |
Arterioveneuze malformaties en fistelsBij arterioveneuze
malformaties en fistels is er een verbinding ontstaan tussen aanvoerende arteriën
en afvoerende venen zonder dat daar een normaal capillair vaatbed tussen zit.
Er is een hoge bloedstroom in deze laesies (high flow). De term
arterioveneuze malformatie wordt gebruikt als het gaat om een
laesie bestaande uit een kluwen van gedilateerde en abnormale vaten met hoge
flow. De term
arterioveneuze fistel wordt gebruikt
als er een directe verbinding is ontstaan tussen een arterie en een vene. Dit
kan congenitaal aanwezig zijn maar ook ontstaan door een trauma, spontaan, of iatrogeen,
bijvoorbeeld
als complicatie na een dotterprocedure. Ook een shunt voor dialyse kan worden
beschouwd als een arterioveneuze fistel. Cerebrale arterioveneuze malformaties
kunnen neurologische klachten veroorzaken zoals epilepsie of beroerte. Bij AV
malformaties in de longen kan hypoxie ontstaan. Bij een grote flow door AV malformaties
kan hartfalen optreden. AV malformaties zijn te herkennen aan klinische kenmerken
zoals warmte of het voelen van pulsaties, en door middel van een echo (duplex).
Combined vascular malformationsGecombineerde vasculaire
combinaties worden genoemd naar de componenten die er in zitten, dus capillair-veneuze
malformatie, capillair-lymfatisch, capillair-arterioveneus, lymfatisch-veneus, capillair-lymfatisch-veneus,
capillair-lymfatisch-arterioveneus, capillair-veneus-arterioveneus, en capillair-lymfatisch-veneus-arterioveneus.
De componenten zijn te herkennen aan de kleur, de vorm, de comprimeerbaarheid en
de flow (pulsaties), zonodig aangevuld met diagnostiek in de vorm van echo, MRI
of biopt.
![Capillair-veneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Capillair-veneuze malformatie](../../../images/capillair-veneuze-malformatie-1z.jpg) |
![Capillair-lymfatische malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Capillair-lymfatische malformatie](../../../images/capillair-lymfatische-malformatie-1z.jpg) |
![Lymfatisch-veneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Lymfatisch-veneuze malformatie](../../../images/lymfatisch-veneuze-malformatie-1z.jpg) |
|
capillair-veneus |
capillair-lymfatisch |
lymfatisch-veneus |
ISSVA classification of vascular tumorsEr is vaak
veel verwarring over de terminologie van vaattumoren en vasculaire malformaties.
De ISSVA (International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies) heeft een
consensus document gemaakt, een PDF bestand,
met een hele duidelijke indeling. Zie de
ISSVA classification
of vascular tumors (PDF). In 2025 is de indeling herzien.
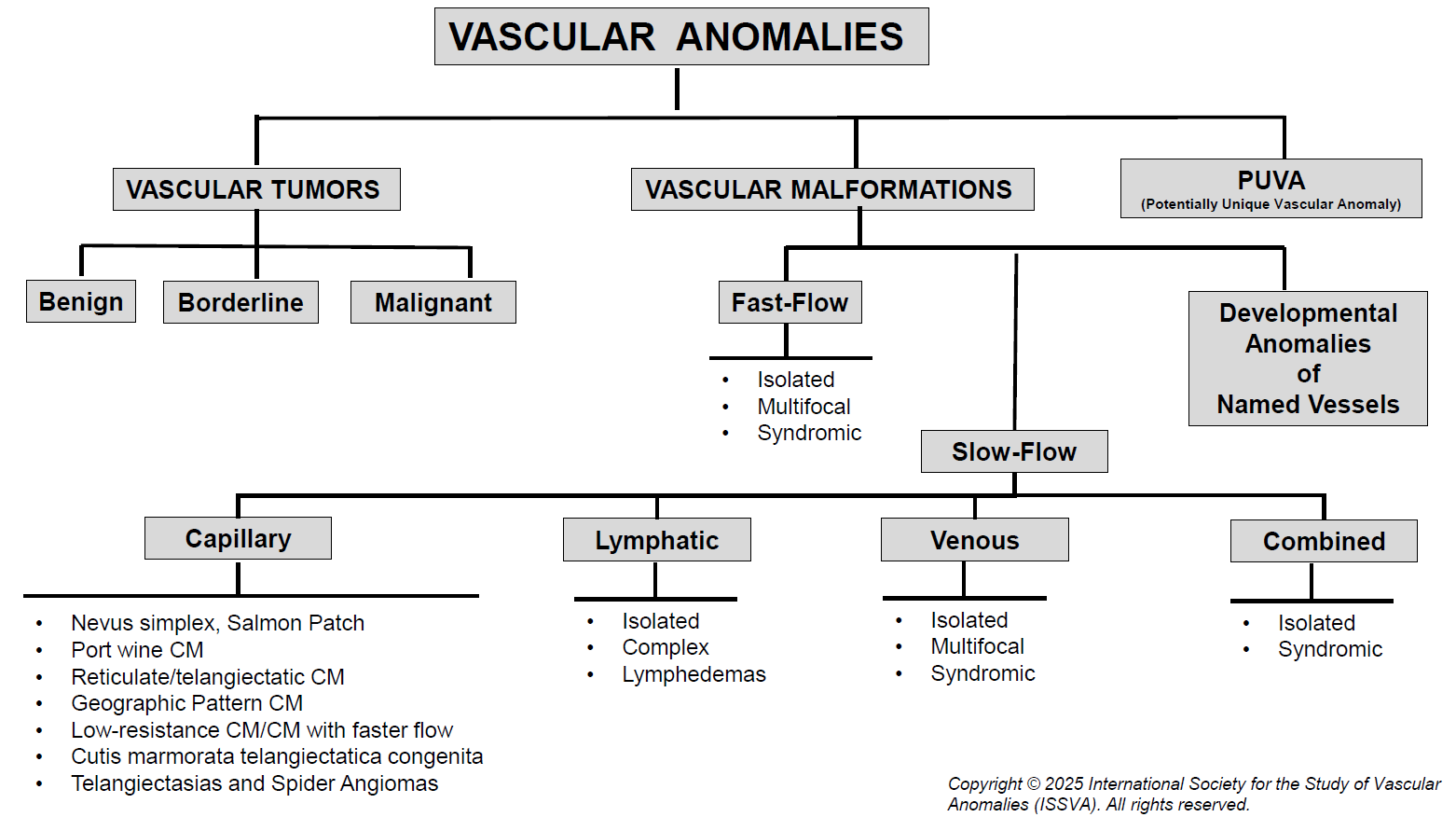
| ISSVA classificatie van vasculaire tumoren: |
Benigne vasculaire tumoren
|
Slow flow vascular malformations
Capillary malformations (CM)
| - |
|
Nevus simplex /
Salmon patch (Angel kiss, Stork
bite) |
| - |
|
Port wine CM (Port wine stain, Port wine
Birthmark,
Nevus flammeus) |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Isolated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Nonsyndromic CM [GNAQ] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
CM with melanocytic nevus (phakomatosis
pigmentovascularis) [GNAQ56, GNA1156, PTPN1157] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Syndromic |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
With hypertrophy or extracutaneous disease (CM with bone
and/or soft tissues overgrowth) [GNA11] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
CM with CNS and/or ocular anomalies (Sturge-Weber
syndrome) [GNAQ] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
DCMO (Diffuse CM with overgrowth) [GNA11] |
| - |
|
Reticulate / telangiectatic CM |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Isolated |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Syndromic |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
M-CM (macrocephaly-capillary
malformation-polymicrogyria) [PIK3CA] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
MIC-CAP (microcephaly-capillary
malformation) [STAMBP] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
DCMO (Diffuse CM with overgrowth) |
| - |
|
Geographic Pattern CM |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Isolated |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Syndromic |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
KTS (Klippel-Trenaunay
Syndrome) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Associated with CLOVES / Disorders of PROS |
| - |
|
Low-resistance CM / CM with
faster flow |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Isolated |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Syndromic |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
CM AVM 1 and 2 (capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Parkes Weber Syndrome |
| - |
|
Cutis
marmorata telangiectatica congenita (CMTC) |
| - |
|
Telangiectasias
and Spider
Angiomas |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Isolated (Telangiectasia) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Syndromic |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
CM-AVM 1 and 2 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
HHT1 [ENG], HHT2 [ACVRL1], HHT3, JPHT
[SMAD4] (Hereditary hemorrhagic
telangiectasia) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lymphatic malformations (LM) |
| - |
|
Isolated |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Common (cystic) LM (Lymphatic malformation)
[PIK3CA] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Macrocystic (cystic
hygroma) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Microcystic (lymphangioma
circumscriptum) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Mixed Macro / Microcystic |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Angiokeratoma |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Channel type LM |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Acquired progressive lymphatic anomaly
(acquired progressive lymphangioma) |
| - |
|
Complex |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
GLA (Generalized Lymphatic Anomaly) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
KLA (Kaposiform Lymphangiomatosis) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
GSD (Gorham Stout Disease) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
CCLA (Central Conducting Lymphatic Anomaly) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Isolated |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Syndromic (RASopathy) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
GLD (Generalized Lymphatic Dysplasia)
[PIEZO1, MDFIC] |
| - |
|
Lymphedemas |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Primary |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Isolated |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Nonne-Milroy syndrome
[FLT4, VEGFR3] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Primary hereditary lymphedema [VEGFC] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Primary hereditary lymphedema [GJC2, Connexin 47] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Syndromic |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Lymphedema-distichiasis
syndrome [FOXC2] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Hypotrichosis-lymphedema-telangiectasia [SOX18] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Primary lymphedema with myelodysplasia [GATA2] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Primary generalized lymphatic anomaly (Hennekam
lymphangiectasia-lymphedema syndrome) [CCBE1] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Microcephaly with or without chorioretinopathy, lymphedema,
or mental retardation syndrome [KIF11] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Lymphedema-choanal atresia [PTPN14] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Secondary |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Venous malformations (VM) |
| - |
|
Isolated |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
VM (Venous malformation) [TEK (TIE2),
PIK3CA] |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Phlebectatic |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
Spongiform |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
VVM (Verrucous
Venous Malformation) [MAP3K3] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
FAVA (Fibroadipose Vascular Anomaly)
[PIK3CA] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Intramuscular venous malformation |
| - |
|
Multifocal |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
VMCM (Familial VM cutaneo-mucosal) [TEK (TIE2)] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
MSVM (Multifocal Sporadic Venous
Malformation) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
BRBNS (Blue rubber bleb nevus (Bean) syndrome) [TEK (TIE2)] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
GVM (Glomuvenous malformation) [Glomulin] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
HCCVM / CCM (Cerebral cavernous
malformation) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
CCM1 [KRIT1], CCM2 [Malcavernin], CCM3
[PDCD10] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
VMOS (Familial intraosseous vascular
malformation) [ELMO2] |
| - |
|
Syndromic |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
PHTS (PTEN Hamartoma Tumor syndrome) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
CLOVES
syndrome (LM + VM + CM +/- AVM + lipomatous overgrowth) [PIK3CA] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Mafucci Syndrome |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Sinus Pericranii |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Combined malformations |
| - |
|
Isolated |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
CLVM (Capillary-lymphatic-venous
malformation) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
LVM (Lymphatic-venous malformation) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
CLM (Capillary-lymphatic malformation) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
CVM (Capillary-venous malformation) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
HCCVM / VVM (Hyperkeratotic Cutaneous
Capillary-Venous malformations) |
| - |
|
Syndromic |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
PROS (PIK3CA Related Overgrowth Spectrum) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
KTS (CLVM with hypertrophy) (Klippel-Trenaunay
Syndrome) |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
CLOVES
syndrome (LM + VM + CM +/- AVM + lipomatous overgrowth) [PIK3CA] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
CLAPO syndrome (lower lip CM + face and neck
LM + asymmetry and partial/generalized overgrowth) [PIK3CA] |
| |
|
|
|
- |
|
Proteus syndrome (CM, VM
and/or LM + asymmetrical somatic overgrowth) [AKT1] |
|
Fast flow vascular malformations
Isolated
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVM) [MAP2K1]
- Intramuscular Fast-flow Vascular Anomaly
- Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) (congenital)
Multifocal
-
CM-AVM 1 en 2 [RASA1, EPHB4]
-
HHT (HHT1 [ENG], HHT2 [ACVRL1],
HHT3, JPHT [SMAD4])
- PHTS (PTEN Hamartoma Tumor syndrome)
Syndromic
- PHOST (PTEN Hamartoma of Soft Tissue) (PHTS)
-
Parkes-Weber syndroom
- SAMS (Spinal Arteriovenous Metameric
Syndrome)
- CAMS (Cerebrofacial Arteriovenous Metameric Syndrome)
|
Combined vascular malformations
| CM + VM |
capillary-venous malformation |
CVM |
| CM + LM |
capillary-lymphatic malformation |
CLM |
| CM + AVM |
capillary-arteriovenous malformation |
CAVM |
| LM + VM |
lymphatic-venous malformation |
LVM |
| CM + LM + VM |
capillary-lymphatic-venous malformation |
CLVM |
| CM + LM + AVM |
capillary-lymphatic-arteriovenous malformation |
CLAVM |
| CM + VM + AVM |
capillary-venous-arteriovenous malformation |
CVAVM |
| CM + LM + VM + AVM |
capillary-lymphatic-venous-arteriovenous malformation |
CLVAVM |
|
Anomalies of major named vessels ("channel type" or "truncal"
vascular malformations)
- Vena cava
- Aorta
-
Vein of Galen
- Others
Affect:
- lymphatics
- veins
- arteries
Anomalies of:
- origin
- course
- number
- length
- diameter (aplasia,
hypoplasia, stenosis, ectasia / aneurysm)
- valves
- communication
(AVF)
- persistence (of embryonal vessel)
|
Vascular malformations associated with other anomalies
- Klippel-Trenaunay
syndrome (CM + VM +/- LM + limb overgrowth) [PIK3CA]
-
Parkes-Weber syndrome (CM + AVF + limb overgrowth) [RASA1]
-
Servelle-Martorell syndrome (limb VM + bone undergrowth)
-
Sturge-Weber syndrome
(facial + leptomeningeal CM + eye anomalies +/- bone and/or soft tissue
overgrowth) [GNAQ]
- Limb CM + congenital non-progressive limb overgrowth
[GNA11]
- Maffucci syndrome (VM +/- spindle-cell hemangioma + enchondroma)
[IDH1, IDH2]
- Macrocephaly - CM (M-CM / MCAP) [PIK3CA]
- Microcephaly
- CM (MICCAP) [STAMBP]
- CLOVES
syndrome (LM + VM + CM +/- AVM + lipomatous overgrowth) [PIK3CA]
- Proteus syndrome (CM, VM
and/or LM + asymmetrical somatic overgrowth) [AKT1]
-
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba
syndroom (AVM + VM + macrocephaly, lipomatous overgrowth) [PTEN]
- CLAPO syndrome (lower lip CM + face and neck LM + asymmetry and partial/generalized
overgrowth) [PIK3CA]
|
Provisionally unclassified vascular anomalies (PUVA)
- Sinusoidal hemangioma
-
Acral arteriovenous
tumor
- Cutaneovisceral angiomatosis with thrombocytopenia (CAT)
|
Referenties
| 1. |
ISSVA. ISSVA classification of
vascular tumors (2014, 2018).
www.issva.org/classification.
PDF |
| 2. |
Kunimoto K, Yamamoto Y, Jinnin M. ISSVA Classification
of Vascular Anomalies and Molecular Biology. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23(4):2358. |
| 3. |
ISSVA. ISSVA classification of
vascular tumors (2025).
www.issva.org/classification.
PDF |
| 4. |
ISSVA Glossary 2025 (lijst van
afkortingen en beschrijvingen van vasculaire malformaties en
tumoren)
www.issva.org.
PDF |
Author(s):dr. Jan R. Mekkes. Dermatologist, Amsterdam UMC.




![Naevus flammeus (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Naevus flammeus](../../../images/naevus-flammeus-4z.jpg)
![Naevus van Unna, ooievaarsbeet (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Naevus van Unna, ooievaarsbeet](../../../images/salmon-patch-2z.jpg)
![Teleangiëctasieën bij levercirrhose (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Teleangiëctasieën bij levercirrhose](../../../images/teleangiectasieen-3z.jpg)
![Capillaire malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Capillaire malformatie](../../../images/capillaire-malformatie-1z.jpg)
![Capillaire malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Capillaire malformatie](../../../images/capillaire-malformatie-2z.jpg)
![Capillaire malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Capillaire malformatie](../../../images/capillaire-malformatie-3z.jpg)
![Veneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Veneuze malformatie](../../../images/veneuze-malformatie-1z.jpg)
![Veneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Veneuze malformatie](../../../images/veneuze-malformatie-2z.jpg)
![Veneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Veneuze malformatie](../../../images/veneuze-malformatie-3z.jpg)
![Veneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Veneuze malformatie](../../../images/veneuze-malformatie-4z.jpg)
![Glomuveneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Glomuveneuze malformatie](../../../images/glomuveneuze-malformatie-1z.jpg)
![Blue rubber bleb nevus syndroom (click on photo to enlarge) [source: Lee C. et al. - Wikimedia - Creative Commons License 2.0] Blue rubber bleb nevus syndroom](../../../images/blue-rubber-bleb-nevus-syndrome-1z.jpg)
![Arterioveneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Arterioveneuze malformatie](../../../images/arterioveneuze-malformatie-1z.jpg)
![Arterioveneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Arterioveneuze malformatie](../../../images/arterioveneuze-malformatie-2z.jpg)
![Arterioveneuze malformatie (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Arterioveneuze malformatie](../../../images/arterioveneuze-malformatie-3z.jpg)
![Histologie arterioveneuze malformatie of hemangioom (click on photo to enlarge) [source: Kevin Kwee / Afdeling Pathologie MUMC] Histologie arterioveneuze malformatie of hemangioom](../../../pacoupes/thumbnails/arterioveneuze-malformatie-1.jpg)
![Histologie arterioveneuze malformatie of hemangioom (click on photo to enlarge) [source: Kevin Kwee / Afdeling Pathologie MUMC] Histologie arterioveneuze malformatie of hemangioom](../../../pacoupes/thumbnails/arterioveneuze-malformatie-2.jpg)
![Histologie arterioveneuze malformatie of hemangioom (click on photo to enlarge) [source: Kevin Kwee / Afdeling Pathologie MUMC] Histologie arterioveneuze malformatie of hemangioom](../../../pacoupes/thumbnails/arterioveneuze-malformatie-3.jpg)
![Arterioveneuze fistel (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Arterioveneuze fistel](../../../images/arterioveneuze-fistel-1z.jpg)
![Arterioveneuze fistel (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Arterioveneuze fistel](../../../images/arterioveneuze-fistel-2z.jpg)
![Arterioveneuze fistel (click on photo to enlarge) [source: www.huidziekten.nl] Arterioveneuze fistel](../../../images/arterioveneuze-fistel-3z.jpg)
