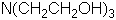
| Formule |
CAS |
| C6H15NO3 |
102-71-6 |
Background
Triethanolamine is used as an excipient in creams, lotions, soaps, shampoos, and bath powders. An excipient is presumably an "inert" substance that gives a topical agent proper consistency through its action as a dispersant or detergent.
Synonyms2,2´,2´´-Nitrilotrisethanol
Triethanolamine
Triethylolamine
Trolamine
TEA
Trihydroxytriethylamine
Tris(hydroxyethyl)amine
UsesCreams and lotions
Cutting oils
Emulsions with mineral and vegetable oil
Herbicides
Lubricants for textile industry
Manufacture of synthetic resins
Petroleum demulsifiers
Pharmaceutic aid (alkalizer)
Shampoos
Soaps
Toilet goods
Waxes
Cross-ReactionsPromethazine
Unusual
Reactions
Back to list of contact allergens
Referenties
| 1. |
Suurmond, D., Patch test reactions to
phenergan cream, promethazine and triethanolamine.
Dermatologica, 1966. 133: p. 503. |
| 2. |
Alomar, A., L. Conde-Salazar, and C.
Romaguera, Occupational dermatoses from cutting oils. Contact
Dermatitis, 1985. 12(3): p. 129-38. |
| 3. |
Jones, S.K. and C.T. Kennedy, Contact
dermatitis from triethanolamine in E45 cream. Contact
Dermatitis, 1988. 19(3): p. 230. |
| 4. |
Tosti, A., et al., Prevalence and sources
of sensitization to emulsifiers: a clinical study. Contact
Dermatitis, 1990. 23(2): p. 68-72. |
| 5. |
Batten, T.L., et al., Contact dermatitis
from the old formula E45 cream. Contact Dermatitis, 1994. 30(3):
p. 159-61. |
| 6. |
Pasche-Koo, F., et al., High
sensitization rate to emulsifiers in patients with chronic leg
ulcers. Contact Dermatitis, 1994. 31(4): p. 226-8. |
Author(s):
Database Allergologie Amsterdam UMC.