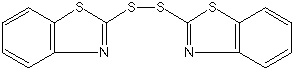
| Formula |
CAS |
| C14H8N2S4 |
120-78-5 |
Background
Dibenzothiazyl disulfide is added to many types of rubber before vulcanization. It is a component of mercapto mix.
Synonyms2,2'-Benzothiazyl disulfide
2,2'-Dibenzothiazyl disulfide
2,2'-Dithiobis[benzothiazole]
Altax
Benzothiazyl disulfide
Dibenzothiazyl disulfide
MBTS
Mercaptobenzthiazyl ether
Naugex MBT
Thiofide
Vulkacit DM
UsesAccelerator for:
- Butyl and styrene-butadiene rubber
- Natural rubber
- Nitrile-butadiene
Retarder for:
- Chloroprene rubber
Adhesives and cements
Antifreeze
Condoms and diaphragms
Cutting oils
Detergents
Disinfectants, repellents, fungicides, and insecticides used in agriculture
Gloves (household, work, or hospital gloves)
Greases
Leather shoes (insoles, adhesives, linings)
Medical devices
Photographic film emulsion.
Renal dialysis equipment.
Rubber in elasticized undergarments and clothing
Rubber pillows and sheets
Rubber shoes (sneakers, tennis shoes, etc)
Soaps and shampoos
Sponge makeup applicators and rubber eyelash curiers
Swimwear
Tires and toys
Veterinarian products like tick and flea powders and sprays
Cross-ReactionsUnusual Reactions
Back to list of contact allergens
Referenties
| 1. |
Foussereau, J., et al., Contact allergy
to safety shoes. Contact Dermatitis, 1986. 14(4): p. 233-6. |
| 2. |
Jung, J.H., et al., Isolation, via
activity-directed fractionation, of mercaptobenzothiazole and
dibenzothiazyl disulfide as 2 allergens responsible for tennis
shoe dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis, 1988. 19(4): p. 254-9. |
| 3. |
Kaniwa, M.A., et al., A method for
identifying causative chemicals of allergic contact dermatitis
using a combination of chemical analysis and patch testing in
patients and animal groups: application to a case of rubber boot
dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis, 1992. 27(3): p. 166-73. |
| 4. |
Hansson, C. and G. Agrup, Stability of
the mercaptobenzothiazole compounds. Contact Dermatitis, 1993.
28(1): p. 29-34. |
Author(s):Allergology: background information on allergens.
