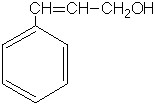
| Formula |
CAS |
| C9H10O |
104-54-1 |
Background
Cinnamic alcohol is a naturally occurring fragrance found in resins and balsams. It is used as a fragrance and flavoring agent for its odor of hyacinth. Cinnamic alcohol is prepared synthetically by the reduction of cinnamic aldehyde. It is found in the free state or as an ester in cinnamon leaves, hyacinth, essence of daffodil flowers, and various other resins and balsams. The International Fragrance Research Association recommends that it be used in a concentration less than 4% because of its sensitizing ability.
The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, present in human skin can convert the cinnamic alcohol to cinnamic aldehyde.
Synonyms3-Phenyl-2-propen-1-ol
Cinnamic alcohol
Cinnamyl alcohol
Styrone
Styryl carbionol
g-Phenylallyl alcohol
UsesCosmetics (particularly soap, deodorants, perfumes and detergents blends, toothpaste)
Foods (chewing gum, cola)
Sanitary napkins
Cross-ReactionsBalsam Peru
Propolis
Unusual ReactionsHyperpigmentation
Back to list of contact allergens
Referenties
| 1. |
Malten KE, van Ketel WG, Nater JP, Liem DH. Reactions in selected patients to 22 fragrance materials. Contact Dermatitis 1984;11(1):1-10. |
| 2. |
Emmons WW, Marks JG Jr. Immediate and delayed reactions to cosmetic ingredients. Contact Dermatitis 1985;13(4):258-265. |
| 3. |
Basketter DA. Skin sensitization to cinnamic alcohol: the role of skin metabolism. Acta Derm Venereol 1992;72(4):264-265. |
| 4. |
Manzur F, el Sayed F, Bazex J. Contact allergy to cinnamic aldehyde and cinnamic alcohol in Oléophytal. Contact Dermatitis 1995;32(1):55. |
Author(s):Allergology: background information on allergens.
