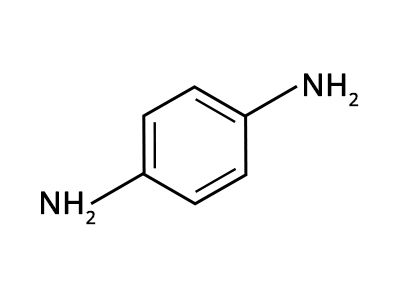
| Formula |
CAS |
| C6H8N2 |
106-50-3 |
Background4-Phenylenediamine base (PPD) is the primary
intermediate in permanent hair dyes and fur dyes. It is an organic compound,
a derivative of aniline. It is used as a component of engineering polymers and
composites, and an ingredient in hair dyes. 4-Phenylenediamine is a precursor
to aramid plastics and fibers such as Kevlar and Twaron. 4-Phenylenediamine
is a common hair dye. The nearly colourless dye precursor oxidizes to the dye.
Also other aniline analogues and derivatives are used such as 2,5-diaminohydroxyethylbenzene,
2,5-diaminotoluene, tetraaminopyrimidine, indoanilines and indophenols. 4-Phenylenediamine
is easily oxidized, and for this reason derivatives of PPD are used as antiozonants
in production of rubber products. A derivative called CD-4 is used as a developing
agent in color photographic film development. PPD is also used as a Henna surrogate
for temporary tattoos.
Synonyms1,4-Phenylenediamine,
4-Phenylenediamine, p-Phenylenediamine, p-Phenyldiamine, Paraphenylenediamine,
PPD, Phenylenediamine base
2-Methyl-p-phenylenediamine, 2-Methyl-para-phenylenediamine
C.I. 76076, C.I. 76042, C.I. 76060
Orsin, Rodol D, Ursol D, Benzofur D, Pelagol
D, Peltol D, Fouramine D, Fourrine D, Furro D, Futramine D, Renal PF, Santoflex
LC, Tertral D
BRN 0774521, CCRIS 7693, CCRIS 509, EINECS 202-442-1, EINECS
203-404-7, HSDB 6251, USAF EK-394, AI3-00710
Oxidation Base 10, Developer
13, Developer PF
Related compoundsToluene-2,5-diamine,
p,m-Tolylenediamine, p-Toluenediamine, p-Toluylendiamine, para-Toluenediamine,
para-Toluylenediamine, para-Tolylenediamine, 2,5-Diaminotoluene, 2-Methyl-1,4-benzenediamine,
4-Amino-2-methylaniline, p-Aminoaniline, 4-Aminoaniline, p-Diaminobenzene, 1,4-Diaminobenzene,
1,4-Benzenediamine, p-Benzenediamine.
UsesCosmetics
(permanent hair colors, some dark-colored cosmetics)
Lithography (printing
inks)
Oils, greases, gasoline
Photocopying
Photographic developers
Primary intermediate in the production of azo dyes
Rarely, fur and leather
dyes
Rubber and plastic industry (antioxidants and accelerators)
Cross-Reactions4-Aminobenzoic acid (PABA)
Para compounds
Parabens
Unusual ReactionsAirborne contact dermatitis
Contact urticaria
Erythema multiforme-like reactions
Photoallergic reactions

References
| 1. |
Temesvari E. Contact urticaria from paraphenylenediamine.
Contact Dermatitis 1984;11(2):125. |
| 2. |
Storrs FJ. et al. Prevalence and relevance
of allergic reactions in patients patch tested in North America
- 1984 to 1985. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1989;20(6):1038-1045. |
| 3. |
Zug KA, Warshaw EM, Fowler JF Jr, Maibach
HI, Belsito DL, Pratt MD, Sasseville D, Storrs FJ, Taylor JS, Mathias
CG, Deleo VA, Rietschel RL, Marks J. Patch-test results of the North
American Contact Dermatitis Group 2005-2006. Dermatitis 2009;20(3):149-160. |
Author(s):dr. Jan R. Mekkes. Dermatologist, Amsterdam UMC.
