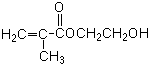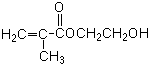
| Formula |
CAS |
| C6H10O3 |
868-77-9 |
Background2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate is a methacrylic
monomer frequently used in UV-curable inks and coatings. It belongs to the group
of plastics, in this case acrylates. Its abbreviation is HEMA. The substance
is used in plastic based dental filling material, in artificial fingernails
manufactured with UV-light cured acrylates, for the production of printing forms
(printing industry) and in acrylic resin laquers. HEMA is indicated to screen
for contact allergy to acrylic-containing nail cosmetics.
Synonyms
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate
HEMA
UsesAdhesives
Artificial nails (UV-light cured acrylates)
Dental filling materials
Acrylic
resin laquers
UV-inks printing forms (printing industry)
Cross-Reactions
Cross reactions possible with other methacrylates
Unusual Reactions
Back to list of contact allergens
Referenties
| 1. |
Clemmensen S. Sensitizing potential of 2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate.
Contact Dermatitis 1985;12(4):203-208. |
| 2. |
Kanerva L, Estlander T, Jolanki R. Sensitization
to patch test acrylates. Contact Dermatitis 1988;18(1):10-15. |
| 3. |
Björkner B. Kontaktallergi för ultraviolett
härdande akrylatprodukter i färger och lacker. Arbete och Hälsa
1989;20:1-39. |
| 4. |
Kanerva L. et al. Occupational allergic contact
dermatitis caused by exposure to acrylates during work with dental
prostheses. Contact Dermatitis 1993; 28(5):268-275 |
| 5. |
Kanerva, L. et al. Statistics of allergic
patch test reactions caused by acrylate compounds, including data
on ethyl methacrylate. American Journal of Contact Dermatitis 1995;6(2):75-77. |
| 6. |
Koppula S, Fellman J, Storrs F. Screening
allergens for acrylate dermatitis associated with artificial nails.
American Journal of Contact Dermatitis 1995;6(2):78-85. |
Author(s):Allergology: background information on allergens.